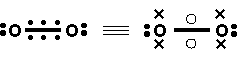
Wavefunction Stability
Example 1 Molecular Oxygen
(i) RHF Calculation
%chk=o2.chk
#RHF/sto-5g scf=qc
O2 singlet
0,1
O
O 1 1.1695
Orbital Symmetries:
Occupied (SGG) (SGU) (SGG) (SGU) (PIU) (SGG) (PIU) (PIG)
Virtual (PIG) (SGU)
E(RHF) =-148.8788617 a.u.
(ii) Test of the wave function stability
#RHF/sto-5g stable guess=read
The wavefunction has an RHF -> UHF
instability.
(iii) UHF Calculation of triplet oxygen
%chk=o2.chk
#UHF/sto-5g scf=qc
O2 triplet
0,3
O
O 1 1.1695
Orbital Symmetries:
Alpha Orbitals:
Occupied (SGU) (SGG) (SGG) (SGU) (PIU) (PIU) (SGG) (PIG)
(PIG)
Virtual (SGU)
Beta Orbitals:
Occupied (SGG) (SGU) (SGG) (SGU) (SGG) (PIU) (PIU)
Virtual (PIG) (PIG) (SGU)
The electronic state is 3-SGG.
E(UHF,triplet) = -148.9626395a.u. (lower than the singlet)
The wavefunction is stable under
the perturbations considered.
Lewis representation (Pauling three-electron bond and Linnett's non-paired spatial orbital structure)
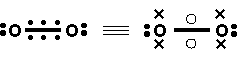
Example 2 Ozone
(i) RHF calculation
%chk=o3.chk
#RHF/6-31G(d) scf=qc
ozone
0,1
O
O 1 1.2227
O 1 1.2227 2 114.0451
Orbital Symmetries:
Occupied (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1) (B1) (B2) (B2)
(A1) (A2)
Virtual (B1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B1) (A1) (B2) (A1)
(A2) (B1) (B2) (A1) (B2) (A2) (A1) (B1) (B2) (A2)
(B1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B1) (B2) (A2) (A1) (B2) (A1)
(A1) (B2) (A1)
The electronic state is 1-A1.
E(RHF)=-224.2585378
The wavefunction has an RHF -> UHF
instability.
(ii) UHF calculation (triplet).
%chk=o3.chk
#UHF/6-31G(d) scf=qc
ozone
0,3
O
O 1 1.2227
O 1 1.2227 2 114.0451
Orbital Symmetries:
Alpha Orbitals:
Occupied (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B1) (A1) (B2) (A2)
(A1) (B2) (B1)
Virtual (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1) (B2) (B1) (A1) (B2) (A2) (A1)
(B1) (B2) (A1) (B2) (A2) (A1) (B1) (B2) (B1) (A2)
(A1) (B2) (A1) (B1) (B2) (A2) (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1)
(B2) (A1)
Beta Orbitals:
Occupied (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1) (B2) (B1) (A2)
(B2)
Virtual (A1) (B1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B1) (A1) (B2)
(A1) (A2) (B1) (B2) (B2) (A1) (A2) (A1) (B1) (B2)
(A2) (B1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B1) (B2) (A1) (A2) (B2)
(A1) (A1) (B2) (A1)
The electronic state is 3-B1.
E(UHF, trip) =-224.2266113\S2=2.062463\S2-1=0.\S2A=2.001812
The wavefunction has an internal instability.
Energy is higher than for the singlet state!
We have to consider an open shell singlet (biradical)!
(iii) UHF calculation (singlet)
%chk=o3.chk
#UHF/6-31G(d) scf=qc
ozone
0,1
O
O 1 1.2227
O 1 1.2227 2 114.0451
Orbital Symmetries:
Alpha Orbitals:
Occupied (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1) (B1) (B2) (B2)
(A1) (A2)
Virtual (B1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B1) (A1) (B2) (A1)
(A2) (B1) (B2) (A1) (B2) (A2) (A1) (B1) (B2) (A2)
(B1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B1) (B2) (A2) (A1) (B2) (A1)
(A1) (B2) (A1)
Beta Orbitals:
Occupied (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (A1) (B1) (B2) (B2)
(A1) (A2)
Virtual (B1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B1) (A1) (B2) (A1)
(A2) (B1) (B2) (A1) (B2) (A2) (A1) (B1) (B2) (A2)
(B1) (A1) (B2) (A1) (B1) (B2) (A2) (A1) (B2) (A1)
(A1) (B2) (A1)
The electronic state is 1-A1.
E(UHF)=-224.2585378
The wavefunction has an internal instability.
We find the same energy and electronic state as in
the RHF calculation.
(iv) We have to consider an open shell singlet (biradical) and we have to destroy a and b spin symmetry.
%chk=o3.chk
#UHF/6-31G(d) scf=qc guess=mix
guess=read stable
ozone
0,1
O
O 1 1.2227
O 1 1.2227 2 114.0451
E(UHF, LUMO HOMO mix)=-224.3272072 a.u. / S2=0.88567
The wavefunction is stable under the perturbations considered.
The wavefunction is contaminated!
(I) VB Bild
a) Lewis

b) Increased Valence structures can be obtained from delocalizing 2 nonbonding electrons into the bonding O-O p LMO.
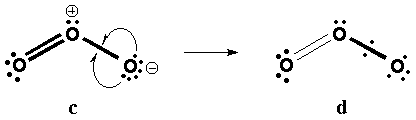
(II) MO: 3-Zentren-4-Elektronen-p-Bindung
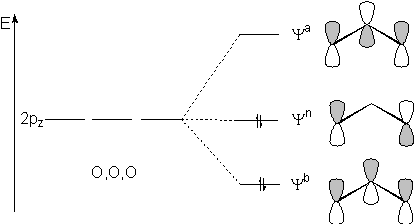
This MO diagram is not correct as the Yn
is
only singly occupied! The biradical character (see VB picture) results
from the coupling singly occupied p orbitals
Summary:
Instabilities can be of many types:
· The lowest energy wavefunction is a singlet, but not a closed shell singlet (e.g. biradical)
RHF Þ UHF instability
· There is a lower-lying triplet state than the singlet (e.g. O2)
RHF Þ UHF instability
RHF Þ UHF instability means E(UHF) < E(RHF)
1O2 : E(RHF) = -149.532997 a.u.
3O2 : E(UHF) = -149.617908 a.u. D
E = 53.3 kcal/mol
· There is more than one solution to the SCF equations for the system, and the calculation converges to a solution which is not the minimum.
RHF Þ RHF instability
or UHF Þ UHF instability
Example Ozone:
· Ozone is a singlet ground state
· Calculation: RHF/6-31G(d) stable=opt
finds: RHF Þ UHF instability
· Calculation: UHF/6-31G(d) stable=opt
finds: UHF Þ UHF instability (internal instability)
· solution: modify the default electronic configuration
(biradical character resulting from the coupling singly occupied p orbitals, a and b symmetry and spatial symmetries needs to be destroyed)
Calculation: UHF/6-31G(d) guess=mix stable
finds: stable wavefunction
last changes: 01.04.2008, AS questions & comments to: axel.schulz@uni-rostock.de